TYPO3 CMS is like the librarian who organizes everything, content, users, and configuration data, in its database, so that your website runs smoothly and efficiently.
TYPO3 database is powerful and organized, from simple blogs to enterprise portals, TYPO3 has a database that makes sure every page loads, every user interaction is tracked and that everything is a precisely where it should be.
Knowing how TYPO3 database works will not only help you run your website better, it will allow you tap into the full potential of the TYPO3 framework.
Ready to discover more about TYPO3's database and learn how it works? Let's dive in!
What is a TYPO3 Database?
Databases act as repositories for information that is stored in an organized manner for easy access, management, and updating. For TYPO3, the database stores all content for your website, including pages, articles, users, settings, and configuration information. In other words, any time you add content through the TYPO3 Backend, it is stored in the database.
TYPO3 Database Structure
TYPO3 organizes its data in columns, fields, and records in a structured way:
- Tables: Think of tables as containers for types of data, for example, TYPO3 tables for pages, content elements, and users.
- Fields: Each TYPO3 table consists of fields, which are the individual pieces of information. For example, a field in the page table could be for the title, description or creation date.
- Records: Each row in a table is referred to as a record, which represents a single piece of data. In other words, one record in the user table represents one user that is registered.
This structure is what allows TYPO3 to easily manage a large amount of content and still keep it organized while being easy to retrieve when necessary.
Key Components of TYPO3 Database
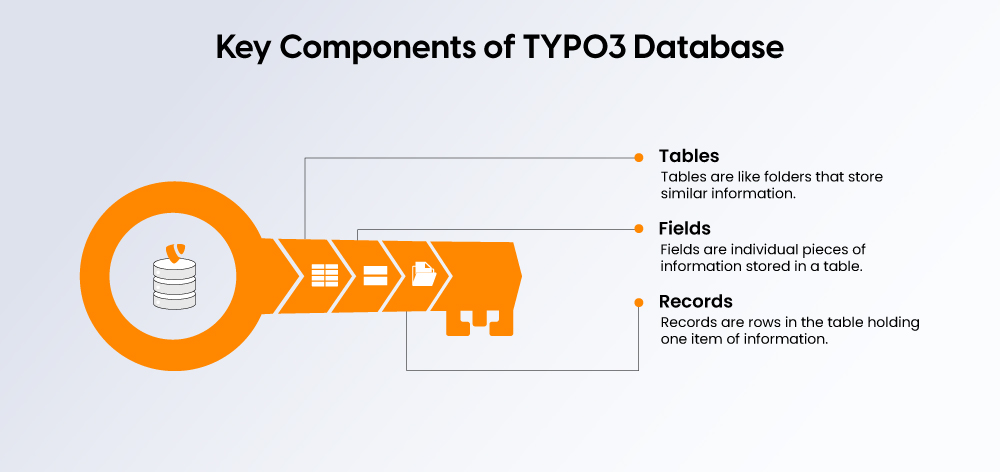
When you get to know the key parts of the TYPO3 database, you understand how all the information on your website is stored and organized. TYPO3 uses tables, fields, and records as basic objects for information storage.
1. Tables
Tables are comparable to folders that store similar information. TYPO3 has numerous tables for storing different types of information. For example:
- Pages table - stores information about all the pages of your TYPO3 website.
- Users table - stores information about the users registered on your website and their permissions.
- Content Elements table - stores the articles, images, or text blocks on your pages.
Each table has a specific function and stores all similar information in one table (or folder).
2. Fields
Fields are the individual building blocks of information stored in a table. You can simply think of a field as a column in a spreadsheet. For example, the Pages table may use the following fields:
- Title - the page title
- Description - the page description
- Created - the date the page was created
Fields allow us to store each individual piece of data uniformly and predictably.
3. Records
Records are the rows in the table that contain an information object. For example:
- A record in the Users table contains information about a user.
- A record in the Content Elements table contains information about an article or a block
Each record contains all the fields for that object and keeps the data organized and easily accessible.
How TYPO3 Interacts with the Database
TYPO3 uses a combination of internal systems and tools to communicate with its database. Understanding this is helpful to see how your website effectively reads, writes, and manages data.
Database Abstraction Layer (DBAL)
TYPO3 uses a component called Database Abstraction Layer (DBAL). The DBAL is the interface to the database and forms the bridge between TYPO3 and the database. Through the DBAL, TYPO3 can communicate with any supported database system such as MySQL or MariaDB.
This means you can write code without having to worry about the underlying database type. This keeps the TYPO3 platform flexible and easier to maintain.
CRUD Operations
CRUD stands for Create, Read, Update, Delete, the universal operations that TYPO3 performs with the database:
- Create: Add new records, e.g., a new page or a new user.
- Read: Retrieve existing records and display them on the website.
- Update: Update existing records, e.g., edit content or change user information.
- Delete: Delete records that are no longer needed.
Every action in TYPO3, adding new content, editing an existing page, or deleting a record, is based on one of these CRUD operation modes. This ensures a clear RDBMS solution for millions of records and is a secure and universal method for data management.
Managing TYPO3 Database Through the TYPO3 Backend
TYPO3 has a simple backend interface that allows editors and administrators to manage website content without having to work directly with the database. The TYPO3 backend is a simplified method for managing the database while keeping your data secure.
TYPO3 Backend Interface
Access to the TYPO3 backend is via a web-based control panel. In the backend, you have access to all the content and settings of your website. Through the backend, you can:
- Add or change pages,
- Manage content elements such as texts, images, and videos,
- Configure users and their permissions.
The backend automatically handles all communication with the database, so you don't have to write SQL commands or edit raw data directly in the database.
Creating, Editing, and Deleting Records
The backend facilitates the management of your database entries:
- Creating records: New pages, content elements, or users can be easily added via a form. When saving the form, TYPO3 automatically creates a new record in the database.
- Editing records: Existing records can be opened in the backend and edited in the appropriate fields. TYPO3 automatically updates the database in the background.
- Deleting records: Records can be deleted in the backend. TYPO3 ensures that the database remains consistent and removes all references to the record if necessary.
The use of the backend is secure and prevents accidental database errors, making it ideal for editors and TYPO3 administrators who do not need direct database access.
Direct Database Access Using TYPO3 phpMyAdmin
The TYPO3 backend facilitates database management, but there are situations where administrators or developers need direct access to the database. This is where phpMyAdmin comes into play.
What is phpMyAdmin?
phpMyAdmin is a web-based management tool for MySQL or MariaDB databases. It provides a visual interface to interact directly with the database: view tables, execute SQL queries, and manage data without having to use the command line.
Why Use TYPO3 phpMyAdmin?
Direct access to the database via phpMyAdmin is particularly valuable for advanced tasks, including:
- Troubleshooting: Quickly check records or analyze issues in the database.
- Backup: Export the entire database or individual TYPO3 tables.
- Manual Edits: Update or correct data that would be difficult to edit in the TYPO3 backend.
This is especially useful for developers or TYPO3 administrators who need deeper access to the database.
Basic Functions in TYPO3 phpMyAdmin
- View TYPO3 Tables: phpMyAdmin displays all TYPO3 database tables. Here you can view the structure of the tables and understand how the data is stored.
- Running SQL Queries: SQL queries can be written and executed to display individual data, update, or delete records.
- Exporting and Importing Data: With phpMyAdmin, you can export the database for backups or import data from one database to another.
- Checking Database Health: Check tables for issues, optimize, and monitor the overall performance of the database.
Using phpMyAdmin provides a powerful toolset to manage the TYPO3 database directly. However, it should be used cautiously to avoid accidental data loss or errors.
TYPO3 Database Security
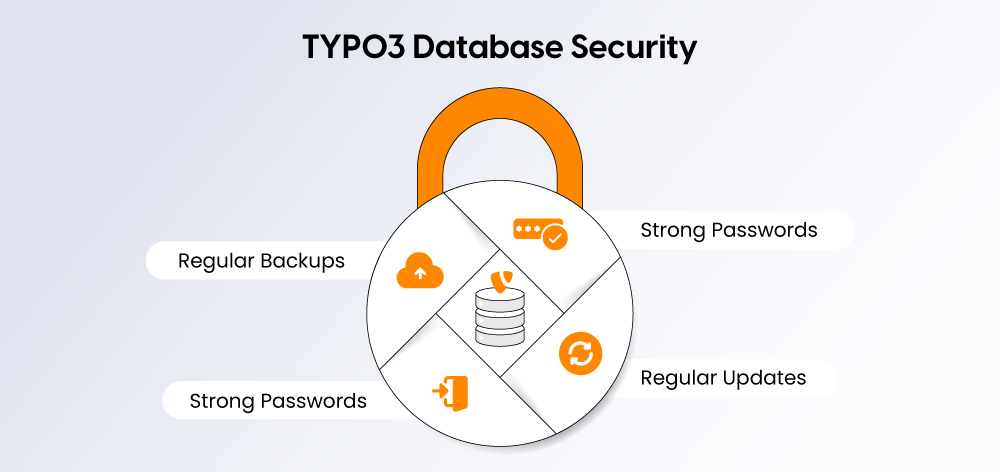
The security of your TYPO3 database is crucial for protecting your website's content, user data, and overall functionality. If the database is compromised, it can lead to data loss, unauthorized TYPO3 access, or even hacker attacks.
The database contains sensitive information such as:
- Website content and pages
- User accounts and passwords
- Configuration settings
- Data from extensions and plugins
If this data is accidentally or maliciously altered, your website may become inoperable or sensitive information could be exposed.
Best Practices for TYPO3 Database Security
To ensure the security of TYPO3, follow these tips:
- Use strong passwords: Use complex, hard-to-guess passwords for all database accounts and avoid default passwords.
- Limit The Access to Database: Ensure that only trusted users and applications have access to the database, and restrict permissions to what is necessary.
- Keep TYPO3 and Database Updated: Keep TYPO3 and the database up to date to close known security gaps. Almost all software updates address current TYPO3 security risks and are therefore safe to install.
- Backups Regularly: Regularly back up the database so that you can easily restore it in case of a problem, and no information is lost.
Following best practices protects your website from attacks or human error, and makes sure that your TYPO3 website runs safely.
Optimizing Database Performance
As your website grows, the database processes more content, more users, and more requests. If it is not optimized, the database can slow down the entire TYPO3 website.
Indexing
The method we use to speed up searching in a database is indexing. An index is like the table of contents of a book, helping the system find the right information without having to flip through every page (or in this case, every record) page by page.
For Example:
- When a visitor performs a search for a page or a content element, these indexes help the database generate the results much faster.
- TYPO3 often automatically creates indexes when triggered, but the administrator can add an index for specific fields if the query is still slow.
Query Optimization
Every time TYPO3 needs to retrieve some data, the query is sent to the database. If these queries are inefficient, the process slows down significantly. There are several ways to optimize queries.
- Ensure that the data is actually necessary (i.e., do not load unused fields).
- Reduce repeated queries through the built-in TYPO3 cache.
- Check slow queries via the database tool (like phpMyAdmin) or MySQL logs at least once a month.
By optimizing the queries and ensuring that the database is properly indexed, the TYPO3 system can remain smooth and responsive even with a large amount of content.
TYPO3 Backup and Recovery
The database is the storage location for all content, users, and settings of your website. If you lose your database, the website must be rebuilt from scratch, which can be time-consuming or even impossible. Regular backups ensure that you always have an up-to-date copy of your data to restore.
How to Backup and Restore your TYPO3 Database
There are two established methods for TYPO3 backups:
- TYPO3 Tools: Some TYPO3 extensions or server tools automate the database backup process. These tools can be scheduled for backups and store the backups either on the server or in external storage.
- phpMyAdmin: phpMyAdmin helps you manage your backups easily and straightforwardly:
- Export: You can export your entire database or specific tables into a file. You can then save this file either on your computer or your TYPO3 backup system.
- Import: If you need to restore your database, you can import the saved TYPO3 backup file back into the database. This resets the website data to the state it was in at the time of the backup.
Best practices would be to store your TYPO3 backups in more than one place (i.e. one on your server and one in cloud storage), and to check and test restoring occasionally to make sure usability of your backups.
Common Issues and Fixing
Like any system that uses a database, TYPO3 can sometimes encounter issues with the database. This information is useful for identifying these issues and ensuring a stable and reliable website.
Common TYPO3 Database Issues
- Missing Records: Records sometimes do not appear in the backend or frontend of your website. This can happen if data was accidentally deleted or if you uninstalled an extension that did not remove the associated data from the database.
- Slow Queries: As growth occurs, some database queries may take longer, often due to the size of your tables or missing indexes.
- Connection Errors: In TYPO3, errors can be displayed if you cannot connect to the database. The cause may be an incorrect TYPO3 login or incorrect connection data for the database, a database server failure, or other configuration issues.
How to Fix TYPO3 Database Issues
1. Missing Records
- If a record is missing, check if it is hidden or disabled in the backend.
- Log in to phpMyAdmin and check if the record exists in the database at all.
- Restore the missing data from a TYPO3 backup if the data was accidentally deleted from the database.
2. Slow Queries
- Use phpMyAdmin to "optimize" the database tables.
- Use phpMyAdmin to add indexes to database fields that require improved search speed.
- Check the TYPO3 logs to see queries that were considered too slow and determine how you can improve these scenarios.
3. For Connection Errors
- Check if the database username, password, and host details are correct in the TYPO3 installation.
- Ensure that the database server is operational.
- If you have recently changed the server, you need to make the appropriate changes in the configuration to update the connection to the new database.
Given checking those common areas, usually most TYPO3 database problems can be fixed in a short time before a major outage occurs.
Conclusion
The TYPO3 database is the backbone of every website built with TYPO3. It stores pages, content, users and settings. It is the focal point that keeps everything chugging along. TYPO3 organizes everything in database tables, fields, and records, all done with simple operations (create, edit, delete records, etc.) that TYPO3 uses to manage the database.
If you think you might want some expert assistance with initial set-up, optimizations, or troubleshooting, you could save a great deal of time and service your database the right way by calling in a professional TYPO3 agency.
Regardless of whether you are maintaining a small TYPO3 website or scaling a huge one, understanding the TYPO3 database will make you work smarter and overcome common mistakes.

Is Your TYPO3 Website Properly Secured?
Learn how to review system updates, user permissions, hosting security, and configuration settings.
FAQ
TYPO3 mainly works with MySQL or MariaDB databases, but thanks to its Database Abstraction Layer (DBAL), it can also connect to other supported database systems.
Yes. The TYPO3 backend lets you create, edit, and delete records using simple forms. You don’t need to know SQL to manage basic content.
phpMyAdmin gives direct access to the database. It’s useful for advanced tasks like running queries, fixing issues, or exporting and importing data.
Use strong passwords, limit who can access the database, keep TYPO3 and the database updated, and make regular backups.
It depends on how often your content changes. For busy sites, daily backups are best. For smaller sites, weekly backups may be enough. Always store backups in more than one location.
Contact for Internet agency and TYPO3 projects
Sven Thelemann
Service Partner - Germany






Be the First to Comment