Recent studies show that around 7.8 million people in Germany, roughly 9.4% of the population, live with a disability. In addition, 22.3% are aged 65 or older and often face difficulties with vision, mobility, or cognition that impact their ability to use digital platforms.
That means nearly 1 in 10 people depend on accessible websites to manage daily activities. It's also important to consider temporary impairments, such as injuries or medical conditions, which can affect anyone at any time.
Web accessibility ensures that digital content and services are usable by everyone, regardless of their abilities. From job applications to online shopping, accessible design removes technical and physical barriers to create equal access for all users; something every TYPO3 agency should prioritize in their projects.
With new accessibility regulations set to take effect in Germany by 2025, ensuring compliance is no longer optional.
In this blog, the key requirements, legal expectations, and actionable steps for creating accessible websites will be explored in detail.
Who Needs to Follow the Accessibility Straightening Act (BFSG)?

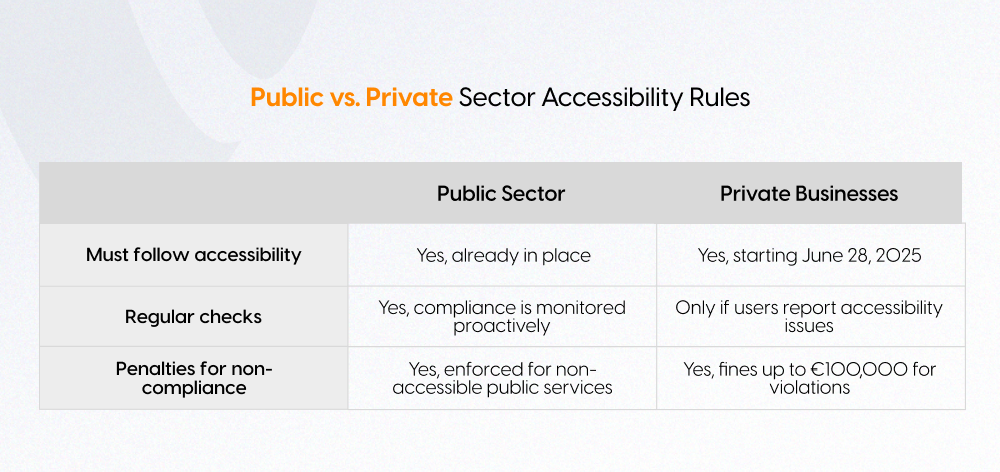
The Accessibility Straightening Act (Barrierefreiheitsstärkungsgesetz or BFSG) is mandatory from June 28, 2025. Various businesses and organization's digital products and services should be accessible to every individual in Germany.
A recent study of 78 of Germany's most visited online stores found that 75% were not fully accessible. One of the biggest issues was the lack of keyboard usability, making it difficult for people who rely on fully keyboard navigation to access. Another evaluation of German online stores gave them an average accessibility score of 67 out of 100 which is well below the recommended standard of 90 or higher.
1. Who Needs to Comply with the BFSG?
The BFSG applies to a broad range of entities, including.
- Companies offering digital services directly to consumers: Any business providing digital services to the public must ensure these services are accessible.
- Public websites, government services, and official platforms: Government agencies and public sector organizations are required to make their digital platforms accessible to all users.
- Websites providing online services or information to the public: This includes platforms that offer information or services to the general public.
2. What Products and Services Are Affected?
The BFSG covers a wide range of digital products and services, such as:
- Websites handling online sales, bookings, or registrations: E-commerce sites, reservation platforms, and any websites facilitating user registrations must be accessible.
- Mobile applications associated with online services: Apps that provide services like banking, shopping, or media access are required to meet accessibility standards.
- Publicly shared digital documents: Files such as PDFs or forms available on websites must be accessible to all users.
Source: activeMind.legal
3. Are There Any Exceptions to the BFSG?
Certain entities may be released from the BFSG requirements:
- Small businesses: Companies that meet specific size and revenue thresholds may be exempted, considering the potential burden of compliance.
- Internal systems: Intranets and internal applications not accessible to the public are generally not required to comply.
- Business-to-business (B2B) platforms: Websites exclusively serving other businesses may be excused in certain situations.
Source:taylorwessing.com
4. What Should Businesses Focus on Now?
To prepare for the upcoming requirements, businesses should:
- Verify relevance: Check whether your technology offerings are indeed within the scope of the BFSG.
- Target improvement: Perform an accessibility review within the scope of an audit to identify essential adjustments.
- Schedule and resolve issues: Form a plan that resolves the accessibility challenges well ahead of the compliance date to avoid last-minute hurdles.
5. Consequences of Non-Compliance
Failure to meet the BFSG can lead to significant fallouts.
- Monitoring and execution: Public websites are subject to regular assessments, while private sites may be reviewed following user complaints.
- Penalties: Non-compliance can result in substantial fines, with penalties reaching up to €500,000 in Germany.
- Reputational damage: Businesses that fail to comply may suffer damage to their reputation, potentially leading to loss of customers and revenue.
By proactively addressing accessibility requirements, businesses can ensure compliance with the BFSG, improve user experience, and avoid potential legal and reputational risks.
Legal Accessibility Guidelines and Requirements

Organizations are provided with a set of guidelines and legal prerequisites to ensure that their web information is available to all users including people with disabilities.
Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.1 and 2.2
As part of the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) set made by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), The WCAG 2.1 which came out in June 2018 made some lower vision and cognitive disabilities mobile accessibility guidelines. In October 2023, WCAG 2.2 also enhanced the accessibility of the content by adding new success criteria to 2.1 improving it further.
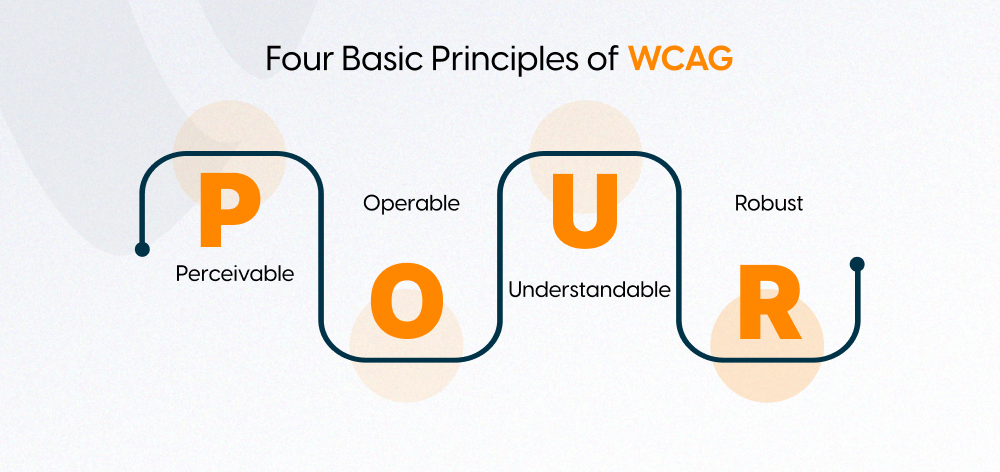
WCAG is organized around four key principles, ensuring that web content is.
- Perceivable: Information must be presented in ways users can perceive, such as providing text alternatives for non-text content.
- Operable: Interference of these components should be possible meaning it is possible to operate via keyboard and delay adequately long for users to read and operate the content.
- Understandable: The Information that can be read and or the operations that are possible in a computer application or the web page provided to the user should be done using simple English words.
- Robust: We need content information is always reliable while being accessed through multiple user agents including of assistive technologies.
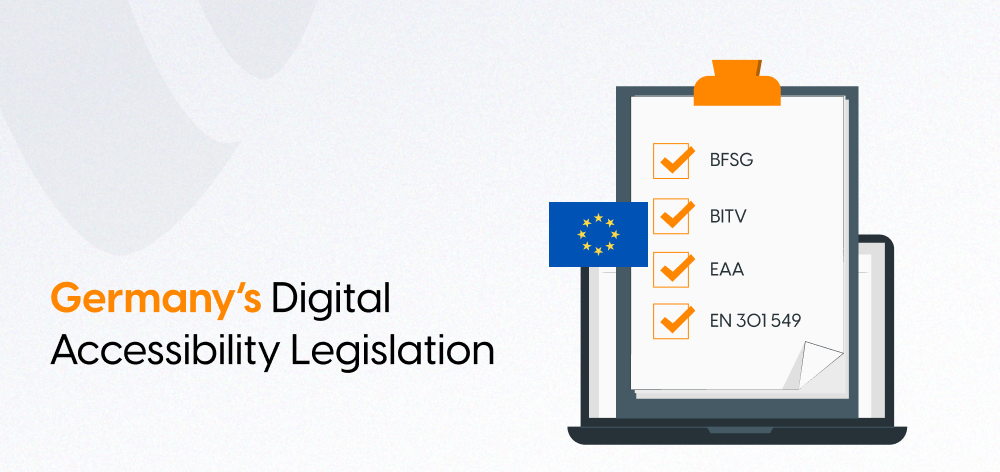
In Germany, there are standing laws that regulate web accessibility, such as the:
- Disability Equality Act (Disability Equality Act - BGG): A law passed to promote equal opportunities for persons with disabilities, the BGG ensures access to various areas such as information technology.
- Barrier-free Information Technology Ordinance (BITV) 2.0: This regulation sets the level of accessible information technologies in compliance with WCAG 2.1. It is meant for use in the public sector for websites and mobile applications and provides access in the following ways: perceivable, operable, understandable, and robust.
- European Accessibility Act (EAA): This is a directive from the EU that seeks to standardize accessibility across all member countries. The EAA has a broader coverage over products and services than any other legislative documents including web and mobile applications with the exception of public procurement.
- EN 301 549: This is a European standard laying down the accessibility provisions for Information and Communication Technology (ICT) products and services. It is meant for public purchasing, but it also integrates WCAG guidelines. It has an impact on national legislation such as BITV 2.0.

WCAG defines three levels of conformance to measure accessibility.
- Level A: The minimum level, addressing basic web accessibility features.
- Level AA: The mid-range level, dealing with the biggest and most common barriers for users.
- Level AAA: The highest and most complex level, addressing the highest level of web accessibility.
Most organizations aim for Level AA compliance, as it addresses the most significant barriers without being as restrictive as Level AAA.
Checklist for an Accessible Website

Technical Requirements
- Use semantic HTML through TYPO3's Fluid templates.
- Make sure responsive designs scale properly on all devices.
- Check the TYPO3 extension for proper ARIA roles and labels.
- Avoid using only color or icons to communicate critical information.
Design and Visual Considerations
- High contrast colors and readable fonts.
- Logical page structure with clear headings and regions.
- Simple language and clear instructions.
- Valid error feedback, especially on TYPO3 forms.
- Ensure alt texts are filled properly, with TYPO3 support in the TYPO3 backend.
Usability and Interaction
- Keyboard Accessibility: All functionalities must be accessible via keyboard.
- Focus Indicators: Visible focus states for interactive elements.
- Time Constraints: Options to extend or remove time limits.
- Form Accessibility: Clear labels, instructions, and error messages.
Media and Alternative Content
- Alt Text for Images: Descriptive text alternatives.
- Captions and Transcripts: Audio and video content.
- Complex Visuals: Detailed descriptions for charts and infographics.
Common Accessibility Mistakes to Avoid

- Images Without Alt Text - Each image must have appropriate alt text that defines what the image contains and its intended use. Do not employ file names such as "image123," or vague words such as "picture." Alt text allows the blind to make use of images through screen readers.
- Not Manually Testing - Automated tools are beneficial, but self-sufficient tools are never faultless. They might overlook certain issues like color contrast or link text which is not defined. Always manually review your website to ensure that it can be navigated easily by all, including those with disabilities.
- Overly Complex Font Styles and Writings - Using decoratively styled fonts is not only easy on the eye, it is also stylish. But for those with dyslexia or low vision, it can be an uncomfortable experience. Excessive blinking animation can be distracting, or even worse, set off epilepsy seizures. Stick to standard fonts that are easy to read and eliminate any movements that are not required.
- CAPTCHA Systems That Are Easiest - Classic CAPTCHAs that make use of graphics, or those that use distorted text alone, exclude users who have visual or cognitive functional problems. A different approach must be taken, such as the implementation of audio-based CAPTCHA, which provides easier ways of moderation.
- Overlooking Mobile Optimization - As many individuals use mobile phones to access websites, it is critical to make sure the process is convenient. Do not use tiny buttons or links that are difficult to press.
Advantages of Accessible Website

- Improves Usability for Everyone - Whether people have disabilities or not, everyone can use and understand the content on an accessible website. Good alt text, clear headings, and easy keyboard navigation are some of the features all users love.
- Keeps You On the Law's Good Side - There are many laws governing accessibility for the web, like the BFSG in Germany or the EN 301 549 for Europe. Making the website accessible helps you follow such rules and avoid legal troubles.
- Upgrades SEO Results - Accessible and well-structured websites always get preferred by the search engines. Having readable text within image pages, having alt texts for images and proper heading structures improves the visibility and ranking in searches.
- Increases Brand Image Significantly - Showing your product on an accessible website depicts that you care about accessibility and user experience which customers appreciate. This enhances the trust in your company's social responsibility and has a positive impact on your brand image.
Helpful Tools to Check Web Accessibility
1 WAVE (Web Accessibility Evaluation Tool)
- Provides visual feedback by highlighting accessibility errors directly on a webpage.
- Helps identify missing alt text, contrast issues, and structural problems.
2 Google Lighthouse
- A built-in Chrome tool that runs audits for accessibility, performance, SEO, and best practices.
- Generates an accessibility score and provides recommendations for improvement.
3. NVDA (NonVisual Desktop Access)
- A free screen reader that allows testing how visually impaired users interact with a website.
- Essential for checking how well a site works with assistive technologies.
4. PDF Accessibility Checker (PAC 2021)
- Scans PDF documents for accessibility issues, ensuring they meet PDF/UA and WCAG standards.
- Useful for businesses sharing reports, brochures, or forms online.
5 W3C Validator
- Checks HTML and CSS compliance with web accessibility standards.
- Helps developers ensure code is structured correctly for assistive technologies.
6. BITV Test
- A German-specific accessibility testing tool that evaluates compliance with BITV 2.0 and WCAG.
- Essential for public sector websites in Germany.
Tools That Help People To Access Websites
Apart from developer testing tools, users with disabilities rely on assistive technologies to navigate the web like:
- Screen Readers - Programs that verbalize text displayed on a computer screen for users who are visually impaired.
- Braille Displays - A device capable of receiving information from a computer and producing a tactile representation of the text using braille letters.
- Keyboard Navigation Tools - These let users use a keyboard rather than a mouse to browse through links and pages using tab and focus indicators.
- Voice Commands - Tools capable of capturing the user's vocal commands and enabling the user to navigate to certain pages, select options, and fill out forms.
- Text Magnifiers - These could be software programs or built in features that increase the size of text, pictures, and other interface components for people with reduced vision.
TYPO3 Accessibility Extensions
Extension | Description | Usage |
Replaces complex CAPTCHAs with user-friendly verification. | Easier form verification for all users. | |
Improves news readability and screen reader compatibility. | Accessible news articles. | |
Ensures accessible labels, error messages, and validation. | User-friendly forms for screen readers. | |
Multilingual, tableless XHTML template compliant with major accessibility standards. | Ideal for government/public websites. | |
Generates menus with access keys and definitions for better navigation. | Improved keyboard-friendly menus. | |
Simplifies adding keyboard shortcuts across your site. | Enhanced keyboard navigation. | |
AI-powered metadata generation and content optimization for accessibility. | Smarter, more compliant content. |
What to Review on Your TYPO3 Website
To make sure your TYPO3 website is accessible to everyone, check these key areas:
- Keyboard Navigation - Make sure users can navigate your site using only a keyboard. Test using the "Tab" key to move through links, buttons, and forms. Nothing should be blocked or skipped.
- Colors and Fonts - Use colors with good contrast so text is easy to read. Choose clear, readable fonts. You can test contrast with contrast checker tools.
- Language Settings - Set the correct language for each page. This helps screen readers read content properly. TYPO3 CMS lets you do this in page properties.
- Headings and Layout - Use proper heading levels (H1, H2, H3) to organize content. This makes navigation easier for users and screen readers.
- Videos and Images - Add captions to videos and alt text to images. This helps users who are blind or hard of hearing understand your content.
- Forms - Make sure all form fields have labels and helpful error messages so users know what to enter. This improves usability for screen reader users.
- Menus and Links - Test if menus and links work with a keyboard and screen readers. Users should be able to navigate without a mouse.
- Resizable Text - Users should be able to increase text size without breaking the layout. Test by zooming in (Ctrl + +) to 200% and checking if everything remains readable and usable.
- Responsive Design - Your website should work well on all screen sizes, including mobile. Make sure elements don't overlap or disappear when resized.
- Alternative for PDFs and Documents - If you upload PDFs or documents, ensure they are accessible by adding text descriptions, proper headings, and searchable text.
By reviewing these areas, you'll make your TYPO3 website more accessible for all users, including those with disabilities.
How to Improve Your TYPO3 Website Accessibility

There are many ways to improve the TYPO3 website accessibility. Below are the key points to ensure your site is accessible, user-friendly, and compliant with accessibility standards.
- Perform an Accessibility Audit - Begin by looking at your website to see how accessible it is and where it falls short. Tools like TYPO3 Accessibility Checker can help automate this process.
- Refer to the Legal Guidelines - When working on the site's templates or adding content, ensure the accessibility standards for the website are met.
- Get Accessibility Extensions - Use TYPO3 extensions that are competent in accessibility to enhance user experience for all.
- Routine Maintenance - Make it a habit to visit the site and ensure it is accessible, especially as layouts and content change over time.
- Train Your Team - Make sure that editors and developers understand how to use TYPO3 accessibility features, such as adding alt tags and using subheadings.
Why Make Your TYPO3 Website Accessible?
- Larger Audience - A compliant website guarantees that all people, including disabled audiences, can easily access and use it.
- Increased Visibility - Websites that have clear hierarchy for the information contained on it and have the content accessible, are most likely to be ranked by the Search Engine.
- Reduced Legal Liabilities - Most countries have implemented policies and laws on accessibility of the internet, hence reducing the chance of being legally impeached by other entities.
- Improves User Experience - People with and without disabilities will have no problem using accessibility features, improving their overall experience on the website.
Conclusion: Make Accessibility a Priority
Web accessibility is very important for providing equal access to all users. Due to the BFSG regulations coming into play, businesses should take action now to make their digital platforms accessible. A website that is well structured and easily accessible enhances user experience and also improves SEO and strengthens brand trust.
Check the changes needed on your TYPO3 website and make sure you employ accessibility compliant tools. The sooner you make these improvements, the better your site will be accessible to every user.
We at NITSAN as a TYPO3 Agency, provide a TYPO3 accessibility solution to ensure your website is accessible to all users. Contact us today for expert guidance to make your site fully compliant and user-friendly!
FAQs:
Use automated tools such as WAVE or Lighthouse and manually check elements such as keyboard navigation, alt texts, color contrasts and form labels.
- Check alt texts for all non-text content.
- Make sure that videos contain subtitles or transcripts.
- Test the color contrast between text and background.
- Navigate the website using the keyboard only.
- Zoom the page to 200% and check the layout for problems.
Perceivable, Usable, Understandable and Robust (POUR). These principles specify how content should be accessible to all users.
Follow WCAG guidelines, use accessibility checkers, test with assistive technologies and conduct regular audits with real users where possible.
Common tools are WAVE, axe DevTools, Lighthouse, Accessibility Insights and screen readers such as NVDA or VoiceOver.
It ensures that people with disabilities can use, understand and interact with websites on an equal footing, while improving SEO and legal compliance.
The Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) are international standards that define how web content should be made accessible for people with disabilities.
Accessible websites often have a better HTML structure, alt texts and faster loading times, all factors that improve search engine rankings.
Missing alt texts, low color contrast, inaccessible forms, incorrect heading structure, missing focus indicators and missing ARIA labels.
An accessibility audit is a structured process for assessing the WCAG conformity and other accessibility standards of a website.
People with disabilities, older users, mobile users, users with slow internet connections and search engines all benefit equally from accessible websites.
ARIA (Accessible Rich Internet Applications) helps to make complex web content and applications more accessible by providing additional information for supporting technologies.
Regularly, especially after major design or content changes, new functions or changes to accessibility legislation.

Contact for SMEs, government organizations and BITV 2.0
Stefan Reinhardt
Service Partner - Germany





Be the First to Comment