Forget the Typical "Which CMS Is Best?" Debate, Let’s Get Real
Instead of the usual chatter about choosing the “right” CMS, we’re diving straight into what really matters. Based on my hands-on experience, TYPO3 offers powerful features that can outshine WordPress in many key areas, especially when it comes to flexibility, scalability, and long-term value.
If you're still reading, you’re probably curious to see what TYPO3 brings to the table.
Let’s dig in and take a deeper look at TYPO3 vs WordPress.
Introduction to Open Source (CMS) Content Management Systems.
A Content Management System (CMS) is software that allows users to create, manage, and publish digital content such as text, images, and videos. It typically includes tools for user management, workflow control, and design customization. CMSs are essential for both small websites and large-scale enterprise platforms.
The global CMS market was valued at $18.2 billion in 2021 and is projected to reach $27.3 billion by 2028, driven by the demand for scalable digital content solutions. Today, over 71% of websites use a CMS, which equates to around 143 million active sites.
(Search Engine Journal)
Choosing the right CMS depends on project goals, technical needs, and team size. A well-implemented CMS can significantly improve productivity by simplifying content workflows and enabling better team collaboration. Studies show that digital platforms can reduce communication and publishing costs by up to 80%.
(Wired)
TYPO3 vs. WordPress: Simple Overview
TYPO3 is a powerful and flexible content management system (CMS), well known for its scalability and enterprise-level capabilities. Originally built for professionals and large businesses that needed advanced control, security, and customization, TYPO3 has evolved.
Today, it's just as suitable for startups and small businesses looking for long-term growth and stability.
On the other hand, WordPress started as a blogging platform but has grown into the most popular CMS globally. Its user-friendly interface makes it ideal for beginners and small to medium-sized websites. However, when projects become more complex, WordPress can show its limitations, this is where TYPO3 often stands out.
If you think TYPO3 is only for large enterprises, think again. A TYPO3 Agency knows there’s a lot beneath the surface that makes it a powerful alternative, even for smaller teams.
Current Core Web Report
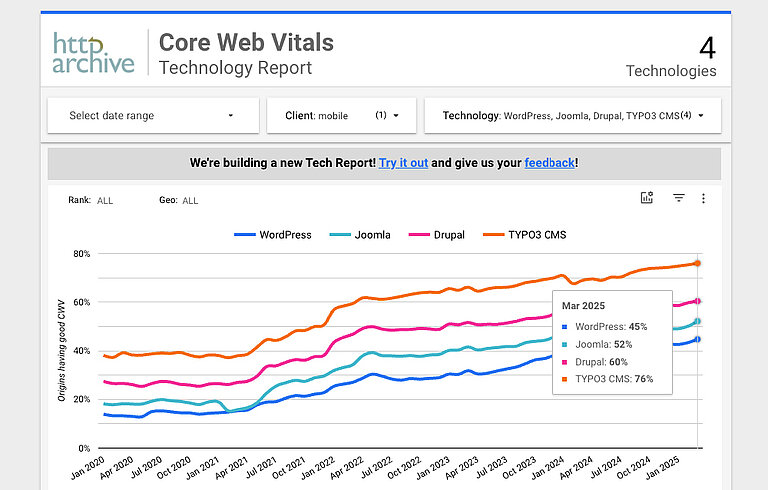
This report covers various aspects of CMS platforms, including WordPress, Joomla, Drupal, and TYPO3 CMS. Click here to access the report and delve into the insights contained within.
TYPO3 vs. Wordpress: The Most Important for Comparison
Safety
Safety always has top priority, and TYPO3 takes it seriously. TYPO3 has built-in security features, regular updates, and a strong community that checks for vulnerabilities. This means that TYPO3 provides better security from the start.
Of course, WordPress is very popular, but it often has security issues. This is due to the use of third-party plugins that can be risky if not well maintained.
Below is a statistic from 2022 showing which CMS platforms are most commonly targeted by hackers. This is mainly due to their lower security and outdated components.
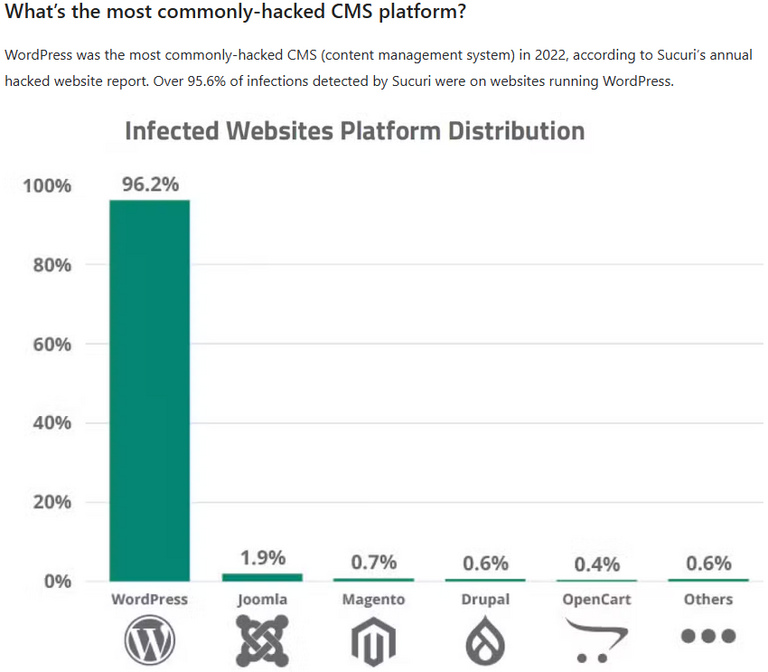
Source: WordPress Hacking Statistics (How Many Websites Get Hacked?)
Performance and Speed
Performance can vary depending on settings, and speed is crucial for user experience and SEO. TYPO3 performs well in this area. It efficiently handles large websites with strong, optimized code.
Additionally, your website's performance can be easily adjusted. Developers can fine-tune every part of the website to ensure smooth operation.
WordPress can also be fast but often requires third-party caching plugins and regular performance monitoring. It may require more effort to achieve the same level of performance as TYPO3.
Multilingual Websites
If you plan to reach a global audience, TYPO3 is the best choice for multilingual websites. TYPO3 has a built-in language management system, making it easy to translate content into different languages without additional plugins or complex settings.
While WordPress can support multiple languages, it often requires additional plugins like WPML or Polylang, which can slow down your website.
Multisite Functionality
Managing multiple websites from one platform is another area where TYPO3 excels. TYPO3's multisite feature allows you to manage different websites under a single installation, saving time and resources.
WordPress offers a multisite feature that is powerful but may require more setup effort. TYPO3 provides more flexibility in managing complex structures, helping businesses operate multiple websites smoothly.
Website Scalability
TYPO3 is designed to grow with your business without limitations. It can easily scale, whether you're adding new pages, users, or features. It's perfect for large companies needing a CMS that can handle complex requirements and high traffic.
WordPress may require more resources, plugins, and custom development for large or complex websites as they grow.
SEO
Both TYPO3 and WordPress offer SEO features, with TYPO3 providing more control over technical SEO elements. You can optimize every part of your website, such as meta tags and URL structures, without needing third-party tools. The built-in TYPO3 AI Extension makes it even easier as it assists with everything.
WordPress has many SEO plugins like Yoast SEO and All in One SEO Pack, making it easy to optimize your website for search engines. However, it lacks built-in SEO functionality for granular control like TYPO3.
Installation
WordPress is known for its quick and easy installation, designed to be user-friendly even for those with little technical knowledge.
While TYPO3 installation may be slightly more complex, there is detailed documentation to guide you through the process. After installation, TYPO3 offers a powerful and flexible platform that can be tailored to your needs.
Templates and Extensions (Plugins)
WordPress has a wide range of plugins for almost every function. However, it would be helpful if it had plugins for almost everything since there are few built-in features.
TYPO3 also has a variety of Best Extensions and TYPO3 Templates, although fewer compared to WordPress. However, it has a highly customizable core standard. TYPO3 extensions are known for their high quality and reliability, designed to provide high performance and security, which can be a challenge with some WordPress plugins.
Responsive Web Design
Responsive web design is crucial in today's mobile-friendly world. TYPO3 makes it easy to create mobile-friendly websites, offering a variety of tools and templates that automatically adapt to different screen sizes.
WordPress also supports responsive design with many Templates and Themes. However, with TYPO3, you have more control over design and layout for all device types.
User Access Permissions
TYPO3 has advanced user access rights, making it ideal for large teams with complex roles. You can create detailed user groups and assign specific permissions to each group, ensuring that everyone has the right level of access.
WordPress also manages user roles and permissions but may not be as precise as TYPO3. TYPO3's user management is more detailed and suitable for large projects.
Certification
TYPO3 offers certification, providing assurance that your website is created and maintained by certified professionals. This is the best thing about TYPO3 to consider.
While WordPress is popular, it is more suitable for personal blogs or small businesses. There is no official certification program, but there is a community of qualified developers who can offer support and services.
Web Accessibility
When it comes to creating accessible websites, TYPO3's Accessibility features are particularly important. TYPO3 closely follows WCAG guidelines, making it easier to create accessible websites for users with disabilities.
Unlike WordPress, which requires multiple plugins to ensure accessibility, TYPO3 provides more control at the core level, helping developers meet legal and user-friendly standards from the start.
TYPO3 vs. Wordpress: Advantages and Disadvantages
Open-source CMS like WordPress and TYPO3 offer a variety of advantages that make them popular options for many companies. The main benefits include:
- Affordability: Free and freely available, making them a cost-effective solution for businesses of all sizes.
- Flexibility: These systems can be easily customized and expanded to meet the specific requirements of a project.
- Community support: Have a large community of developers and users who provide support and resources.
However, there are also some disadvantages to consider:
- Security risks: Can be vulnerable to security vulnerabilities if not regularly updated. It is important to install security updates and patches for TYPO3 promptly.
- Complexity: Can be complex and require technical expertise for management and customization. This can be a challenge for users without technical knowledge.
Websites Built on TYPO3 and WordPress
TYPO3 is used by large organizations such as universities, government institutions, and multinational companies thanks to its scalability and reliability.
An example of this is a client who chose TYPO3 for their corporate website to meet specific requirements and previous experiences.

Popular Websites Created with TYPO3:
WordPress is the foundation for many blogs, small businesses, and e-commerce websites. However, for high-traffic and complex websites, TYPO3 is a more powerful solution.
Check out this comprehensive guide: How to create your website with TYPO3

TYPO3 and WordPress: Breakdown of the Statistics
With over 40% of all websites on the internet, WordPress is a popular CMS. Its popularity shows how easy it is to use and how flexible it can be.
TYPO3, while less widespread than WordPress, has a dedicated user base, including some of the world's largest websites. It is used by over 500,000 websites worldwide, proving its value for large, enterprise-wide websites.
TYPO3 vs. WordPress: Side-by-Side Comparison
Feature | TYPO3 | WordPress |
Ease of Use | Requires technical knowledge | User-friendly |
Customization | Highly customizable | Extensive plugins |
Community support | Smaller community | Large community |
Security | Built-in security features | Relies on plugins |
Performance | Efficient for large sites | Optimizable with plugins |
Multilingual support | Built-in support | Requires plugins |
Multisite | Built-in capabilities | Supported but less flexible |
SEO | Built-in tools | Plugins needed |
Installation | More complex | Easy installation |
User access | Advanced | Basic to intermediate |
Scalability | Excellent for large projects | Good for small to medium sites |
Functions that TYPO3 Offers, but WordPress Does Not
Here I would like to mention the functions that WordPress does not offer, but TYPO3 provides by default. Since TYPO3 is a real CMS tool, adapting web design in the TYPO3 system often requires the support of a programmer to modify the template accordingly.
1. Workspace
If your website has a large number of pages and content, and you have a large team to manage them, you can set up this great function of the TYPO3 backend. This is a simple workflow or lifecycle that you can set up to ensure that any changes made by an editor must be approved by a reviewer.
With the custom workspace, you have many advantages such as security, transparent versioning, preview, overview of changes, and thus a state-of-the-art content management.
2. History / Undo
You can undo your changes and restore the original state. To undo the deletion of an element, you must use the History/Undo function for the entire page. This option opens the Rollback feature, which lists all changes made to the page.
3. TYPO3 Logs
In the TYPO3 backend, there is a section that displays the list of actions, errors as logs, changes, etc. This can help the administrator review the changes in each content/element. The administrator can determine who made the changes. It also logs the login and logout details of users. This way, the administrator can check who logged in at what time and what changes they made.
4. Copy/Paste (Content Elements, Records, etc.)
While WordPress recently introduced the copy and paste of elements, TYPO3 has offered this feature for years. You can copy and paste elements from one page to another or add a reference to any element to reuse it. Additionally, TYPO3 offers the ability to copy and paste the element as a reference. This way, you only need to change the content in one place, and the changes can be applied to all affected elements/contents. This can save a lot of time.
5. Forms
For any CMS, it is necessary to create various types of forms. You should not depend on a third-party or external plugin. By default, WordPress does not offer this basic form function.
TYPO3, on the other hand, offers form management by default. This allows you to create an unlimited number of forms and use them.
6. Clipboard
Every time a record is copied into the TYPO3 CMS backend, TYPO3 also provides access to its internal clipboard. So you can put everything in the clipboard and also retrieve information from it. It is the core API, so you can use and extend it for your own extensions.
7. Internal Search Engine
TYPO3 provides the search engine by default. It is called Indexed Search. Indexing helps with HTML data priority, word count and frequency for evaluating results, exact, partial, or metaphonic search, etc. And the search plugin helps in searching for whole words, word parts, sounds, phrases, language-dependent search, and much more.
8. LDAP/SSO Authentication (Backend and Frontend User Authentication)
TYPO3 supports LDAP authentication and makes TYPO3 a secure CMS. TYPO3 LDAP/SSO authentication allows importing/updating/deleting users and groups (frontend, backend, or both) from an LDAP directory and provides Single Sign-On (SSO) for frontend users. These features make it the perfect choice for using TYPO3 as an intranet CMS.
9. User Management, Frontend Users & Login
As mentioned earlier, CMS WordPress does not offer much when it comes to user and role management. TYPO3 offers a range of configurations, settings, and features for roles, user management, access permissions, frontend users, and standard TYPO3 Login module. So, for basic things, you do not need to rely on a third-party tool.
10. Powerful Built-in Cache
Since TYPO3 CMS 4.3, one of the key components of TYPO3 is the data caching framework for better website speed. TYPO3 can cache frontend content and pages.
What Makes TYPO3 So Special?
The strengths of TYPO3 lie in its flexibility and scalability, making it the top choice for large, complex websites.
- Flexibility and scalability: Ideal for large, complex websites.
- Advanced user access permissions: Provides detailed user management.
- Integrated multilingual support: No additional TYPO3 Extension required for language functions.
- Advanced features and high security: Perfect for companies needing robust features and security.
- Growth-friendly: Designed to grow with your business over time.
- Built-in features: Unlike CMS WordPress, which heavily relies on plugins, TYPO3 has built-in features that can be used immediately.
If you are looking for a CMS that can meet complex requirements and grow with your business, TYPO3 is the right choice.
Want to know about your TYPO3 Version? Check out this guide on How to Check and Manage Your TYPO3 Version
The Future of Content Management Systems TYPO3 or WordPress
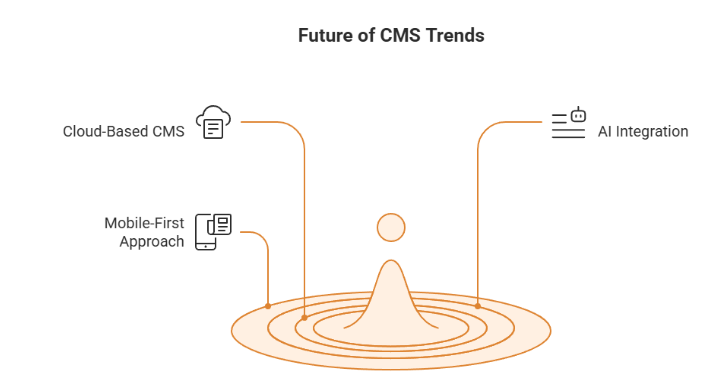
The future of content management systems looks promising, with an increasing demand for flexible and scalable solutions. Some of the trends that will shape the future of CMS are:
- Cloud-based CMS: Cloud-based CMS offer a variety of benefits, such as scalability and flexibility. They allow companies to manage their content from anywhere and provide high availability and reliability.
- Artificial Intelligence: Artificial intelligence is increasingly being integrated into CMS to automate content creation and management. This can increase efficiency and provide personalized content for users.
- Mobile-First Approach: The Mobile-First approach is becoming increasingly important as more users access content through mobile devices. CMS must be able to create mobile-friendly websites that work well on different devices.
Selecting the Right CMS: A Checklist
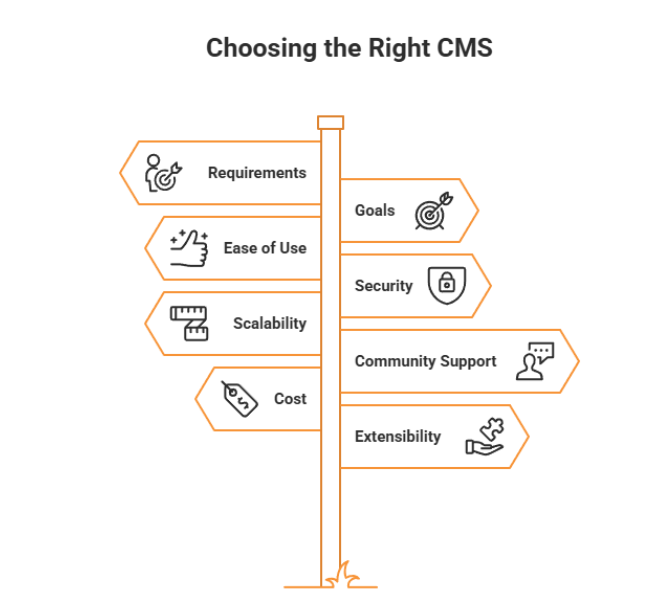
The selection of the right CMS depends on the individual requirements and goals of the project. Here are some factors to consider when choosing a CMS:
Criteria | Key Questions |
Requirements | Does it support multilingual content, user roles, and SEO features? |
Goals | Can it grow with your business and adapt to new needs in the future? |
Ease of Use | Is it beginner-friendly and usable by non-technical staff? |
Security | Does it offer strong security features and regular updates? |
Scalability | Can the CMS handle growth in content, traffic, and functionality? |
Community Support | Is there a large, active community for support, tutorials, and resources? |
Cost | What are the initial and long-term costs (setup, maintenance, upgrades)? |
Extensibility | Are there many reliable plugins or modules to extend functionality? |
This checklist can help you choose the correct CMS for your project and ensure it meets your requirements and goals.
Conclusion
Thank you for reading our article!
We hope this article has helped you find the perfect CMS for your needs! If you have any further questions, we are here to help. At NITSAN - TYPO3 Agency, an expert team with over 14 years of experience in TYPO3 services is available to you.
Stay tuned for more updates - we have much more in store!
Need further assistance? Simply fill out the form below, and we will get back to you! Your thoughts are important to us, so please share them with us!
Do you need further assistance? Simply fill out the form, and we will get in touch with you! Your thoughts are important to us, so please share them with us!
FAQs
TYPO3 is designed for scalability and enterprise-level projects with advanced customization, while WordPress is user-friendly and ideal for small to medium websites.
Yes, TYPO3 has evolved to support businesses of all sizes, offering long-term stability and growth potential even for smaller teams.
Both require regular updates for security, but TYPO3 is often favored in enterprise environments for its robust built-in security features.
TYPO3 has a steeper learning curve compared to WordPress, but with proper training, non-technical users can manage it effectively.
A strong community offers valuable resources, plugins, and troubleshooting help. Both TYPO3 and WordPress have active communities, but WordPress’s is larger.
Consider your project’s complexity, scalability needs, team expertise, security requirements, and long-term goals when choosing the right CMS.
Contact for Internet agency and TYPO3 projects
Sven Thelemann
Service Partner - Germany






Be the First to Comment